BONE MARROW TRANSPLANT
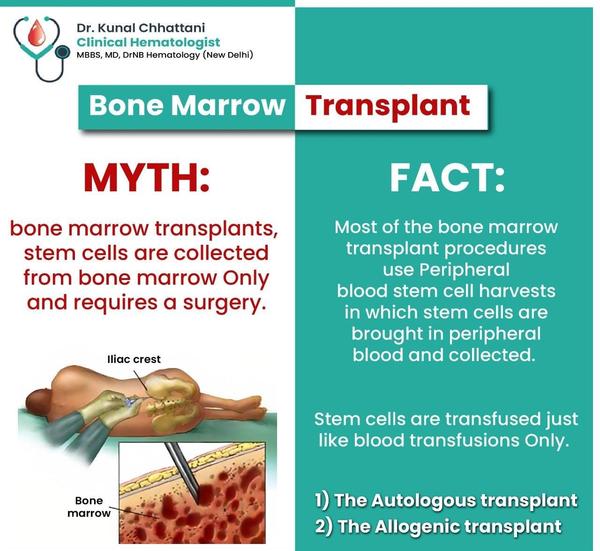
A Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT) is a medical procedure to replace damaged or destroyed bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. The new marrow can either come from:1. Your own body (Autologous transplant)2. A donor (Allogeneic transplant) Why is BMT Done?To treat conditions where the bone marrow is not functioning properly, such as:1. Blood cancers: Leukemia, Lymphoma, Multiple Myeloma2. Bone marrow failure syndromes: Aplastic anemia3. Genetic disorders: Thalassemia, Sickle Cell Anemia4. Immune deficiency disorders🩸 Types of Bone Marrow Transplant1. Autologous BMT: Uses the patient’s own stem cells. Common in cancer treatment.2. Allogeneic BMT: Uses stem cells from a donor (sibling or unrelated match).3. Haploidentical BMT: Uses a half-matched donor (like a parent).4. Umbilical Cord BMT: Stem cells are taken from a baby's umbilical cord after birth.🏥 Steps in BMT Procedure1. Pre-transplant Evaluation2. Conditioning Therapy (high-dose chemo or radiation to destroy diseased cells)3. Stem Cell Infusion (like a blood transfusion)4. Engraftment (stem cells grow and start making healthy blood cells)5. Recovery and Monitoring⚠️ Risks & Complications1. Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (in allogeneic BMT)2. Infections3. Organ damage4. Bleeding or anemia5. Relapse of original disease🛡️ Post-Transplant Care1. Isolation initially to prevent infections2. Regular blood tests and checkups3. Immunosuppressants (in case of allogeneic transplant)4. Nutritional support
READ MORE